The Digital Skills Lab offers support in a range of specialist research tools. See below to find out what's on offer. If you need help with a specific tool not listed, please email digital.skills.lab@lse.ac.uk to see how we can help.
If you need help with NVivo, SPSS, Stata or Qualtrics, check out the Digital Skills Lab drop-in sessions via Teams.
Tools for Data Collection
There are many useful tools for collecting data for research and it is important that you consider ethical issues related to data collection, including permissions and GDPR regulations. See the relevant section below for more information.
Qualtrics is a powerful survey tool for collecting and analysing information. Access to Qualtrics is available for LSE staff, postgraduates and some undergraduates – the Data and Technology Services (DTS) web pages have more information on requesting an account.
The Digital Skills Lab recommends the following help guides for Qualtrics:
Qualtrics also offer a range of free online training courses. We recommend:
The Digital Skills Lab also run drop-in sessions for coding and research software, where you can speak to one of our Trainers for advice and support.
The Library Research Management team offer courses throughout the year on all aspects of data management. Contact Hannah Boroudjou for more information about support available.
If you are conducting research interviews remotely, there are tools in both Zoom and Microsoft Teams to help create transcripts. Before using them, you should ensure you consider the ethical issues around recording interviews and using automated transcription services:
Key issues to consider:
- Permission must be sought from all participants in a video call before it can be recorded and shared outside the original group. When collecting personal data, it is advisable to seek written consent. For example, if you are conducting interviews with research participants via Zoom, Skype or MS Teams you could ask permission in the informed consent to record the sessions.
- GDPR states that data collection should be adequate, relevant and not excessive i.e. only collect what data you need. If you're collecting research data via Skype/ Zoom etc then you should consider whether you need to record video or whether audio alone would do. Audio recordings still count as personal data but they are less sensitive than video recordings.
- Please also ensure that you have set up any video recording software in line with GDPR regulations. Please see our guides to doing research online for undergraduate and MSc Students and for Researchers.
- Before you use any software for transcription please contact the Research Data Librarian at datalibrary@lse.ac.uk, they can check whether the tools you’re using are secure and compliant.
If you will be using social media posts as part of your research, you should first consider the ethical issues associated.
The School has published guidance for researchers regarding minimum standards – see Research Tools Minimum Standards, particularly the section about Content scrapers
Key rules for social media:
- You must ensure you check the terms and conditions of individual social media platforms before you begin harvesting data from them. The LSEs Guidance on social media, data protection and research includes a summary of terms and conditions of researchers for each platform
- Researchers often assume that because social media content has been posted publicly that means it’s fair use to reproduce it in research. However, that is not the case. You must seek permission from individual users before you re-use their data in your research (including unpublished research like dissertations).
- Please separate out identifiable data I.e. social media handles and IDs from any social media data you have harvested as early as possible.
- Bear in mind that removing Social media handles/ IDs may not be enough to ensure individuals are not identifiable. For example, users may be identifiable via a direct quote if copied and pasted into Google.
- For more guidance about the ethics of using social media data in research please see Social Media Research: A guide to Ethics, from the University of Aberdeen.
- A useful guide to making decisions about seeking permission for publishing tweets.
Which tools?
A great starting place for understanding methodologies, tools, and related issues is this post on the LSE Impact Blog, Using Twitter as a Data Source: An overview of social media research tools 2019 by Dr Wasim Ahmed. Although focussed on Twitter, he recommends several tools and techniques that can be used on multiple platforms.
Support and training available:
The LSE Library has secured a licence to use ProQuest TDM Studio. ProQuest TDM Studio is a platform for text and data mining across the Library's current ProQuest subscriptions. Features of the ProQuest TDM Studio platform include:
- Access data from the ProQuest library of resources, which includes videos, books, journal articles, and newspapers
- Use pre-made scripts to extract the data you want
- Either extract the data to use in a different platform, such as NVivo or QDA Miner, or do analysis within the TDM Studio environment using R and Python
- The workbench dashboard feature allows analysis to be done across the majority of the Library's ProQuest subscriptions using R and Python
- Visualisation dashboard has a graphical user interface with pre-built visualisations
ProQuest TDM Studio is available by request only. To request an account, contact the data library.
Tools for Data Analysis and Visualisation
Are you using qualitative or quantitative data for your research project and don’t know which tool to use for analysis? See below for a brief overview of recommended tools.
Qualitative data
Qualitative data is defined as non-numerical data, such as text, video, photographs or audio recordings. This type of data can be collected using diary accounts or in-depth interviews, and analyzed using grounded theory or thematic analysis (qualitative analysis). Qualitative data can also be analyzed using mixed methods, allowing you to use quantitative analysis on qualitative data. Use our Text Analysis Tool decision tree to determine which tools might be right for you:
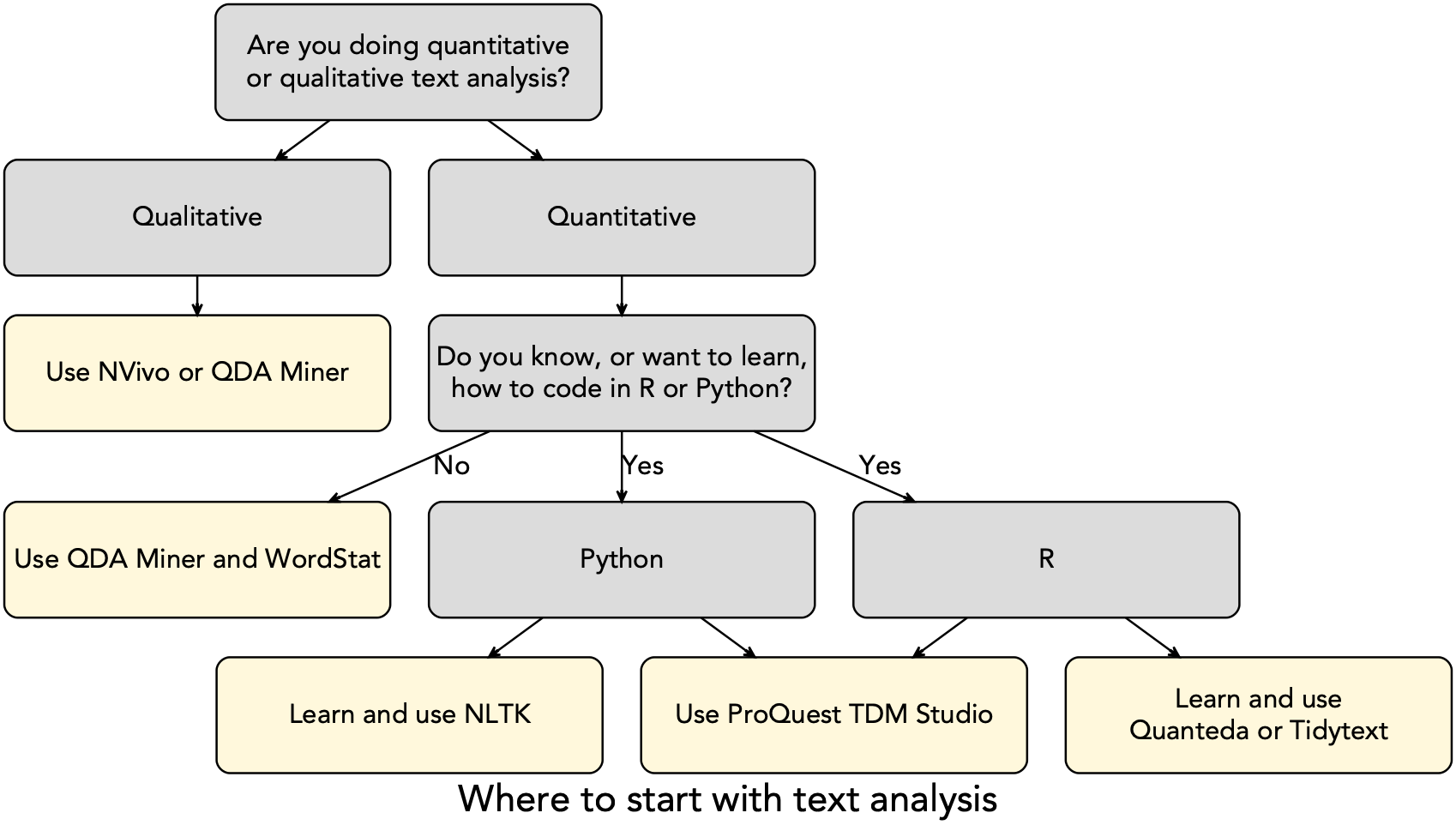
Text Analysis Tools for Qualitative Analysis
NVivo is a commercial software that provides tools for qualitative and mixed methods analysis. Features of NVivo include:
- Management and analysis of textual, audio, video, image, email, and spreadsheet data
- Tools for automatic identification of themes and sentiments
- Text and coding queries tools, as well as cross-tabulation
- Make mind, concept, and project maps
- Create visualisations such as word clouds, tree and sunburst maps, cluster maps, and bar or pie charts
The Digital Skills Lab has commissioned a self-study Introduction to NVivo Moodle course which covers the basic steps needed to set up an NVivo project, add textual data and code. The course consists a series of videos together with step-by-step guides, some sample data and a completed NVivo project. QSR have a created a number of YouTube playlists of tutorials and webinars for multiple versions of NVivo for both Mac and Windows.
Please contact DTS to request a personal licence.
QDA Miner is a commercial software used for mixed methods analysis. It provides quantitative tools for analysing qualitative data, as well as the common qualitative tools for qualitative data analysis that you see with software like NVivo. QDA miners features include:
- Powerful and flexible tools to assist with coding and dealing with coded data
- Easy to use text searching and writing tools
- Easy to use exporting features (exporting data, visualisations, or tables for example)
- Geocoding, allowing the linking of geographical locations and corresponding temporal dimensions
- Wide variety of visualisation types and styles
- Add-on features such as Wordstat
- Able to handle multiple data types in multiple formats, such as text, image, database, reference manager (for example Endnote, Mendeley or Zotero), web survey data, online sources such as social media
Provalis Research have a number of free video tutorials and demos that will help you familiarize yourself with the basics and some advanced features of QDA Miner.
QDA Miner is available on the LSE Remote Desktop. Please contact DTS to request a personal licence.
Text Analysis Tools for Quantitative Analysis
QDA Miner is a commercial software used for mixed methods analysis. It provides quantitative tools for analysing qualitative data, as well as the common qualitative tools for qualitative data analysis that you see with software like NVivo. QDA miners features include:
- Powerful and flexible tools to assist with coding and dealing with coded data
- Easy to use text searching and writing tools
- Easy to use exporting features (exporting data, visualisations, or tables for example)
- Geocoding, allowing the linking of geographical locations and corresponding temporal dimensions
- Wide variety of visualisation types and styles
- Add-on features such as Wordstat
- Able to handle multiple data types in multiple formats, such as text, image, database, reference manager (for example Endnote, Mendeley or Zotero), web survey data, online sources such as social media
Provalis Research have a number of free video tutorials and demos that will help you familiarize yourself with the basics and some advanced features of QDA Miner.
QDA Miner is available on the LSE Remote Desktop. Please contact DTS to request a personal licence.
Wordstat is an add-on to QDA miner, that provides sophisticated content analysis and text mining tools. Wordstat is ideal for those looking to quickly extract and analyse information from large amounts of data. Some of its features include:
- Text mining tools that provide fast extraction of themes and patterns
- Ability to handle multiple different data types, such as documents, online sources, data files, web surveys, and reference managers
- Topic modeling
- Able to relate text with structured data
- Make or use dictionaries to categorise words or phrases
- Integration with machine learning models such as K-Nearest Neighbours
Provalis Research have a number of free video tutorials and demos that will help you familiarize yourself with the basics and some advanced features of WordStat.
Please contact DTS to request a personal licence.
Text Analysis with Python
If you're not familiar with Python but would like to learn for text analysis, the Digital Skills Lab offers taught workshops that are run weekly during Autumn and Winter terms, and on an ad hoc basis the rest of the year. If there are no workshops running or you would prefer self-study on your own time, the Digital Skills Lab have curated a number of free resources which can be found in the Python Collection on Moodle.
Python is an open-source general purpose programming language, with many software extensions known as libraries. Text analysis in Python is achieved using the Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK) library. NLTK is a free, open-source platform for building Python programs to work with human language data.
The NLTK creators have a free open source tutorial and documentation on what you can do with the NLTK library. The Digital Skills Lab are working on an introductory course and we recommend you sign up to the newsletter so you are notified once it is available.
The LSE Library has secured a licence to use ProQuest TDM Studio. ProQuest TDM Studio is a platform for text and data mining across the Library's current ProQuest subscriptions. Features of the ProQuest TDM Studio platform include:
- Access data from the ProQuest library of resources, which includes videos, books, journal articles, and newspapers
- Use pre-made scripts to extract the data you want
- Either extract the data to use in a different platform, such as NVivo or QDA Miner, or do analysis within the TDM Studio environment using R and Python
- The workbench dashboard feature allows analysis to be done across the majority of the Library's ProQuest subscriptions using R and Python
- Visualisation dashboard has a graphical user interface with pre-built visualisations
ProQuest TDM Studio is available by request only. To request an account, contact the data library.
Text Analysis with R
R is an open-source programming language for statistical computing and graphics, with many software extensions known as libraries or packages. There are two libraries that have been built for text analysis with R: Quanteda and Tidytext and information on each is below.
Not sure whether to use Quanteda or Tidytext? If speed is an important consideration, then Quanteda is the package you should go for. Both packages link up well with Tidyverse such as use of tibbles and pipes.
If you’re not familiar with R but would like to learn it for text analysis, the Digital Skills Lab offers taught workshops that are run weekly during Autumn and Winter terms, and on an ad hoc basis the rest of the year. If there are no workshops running or you would prefer self-study on your own time, the Digital Skills Lab have curated a number of free resources which can be found on Moodle, such as Codecademy’s learn R course. The Digital Skills Lab would also recommend the R for Data Science book, which is available for free online.
Developed by Professor Ken Benoit, Director of the LSE Data Science Institute, the quanteda package has a useful set of tools for processing and analysing textual data. These free quanteda tutorials will help you to:
- Learn how to import various types of text data into R
- Learn basic operations in quanteda
- Learn how to perform statistical analysis using quanteda
- Learn how to combine operations and analysis in quanteda
- How to derive latent positions from text data and how to classify documents
- Learn pre-processing of texts in different languages
Developed by Julia Silge, Data Scientist for RStudio, the Tidytext package like quanteda has a useful set of tools for processing and analysing textual data. These free tidytext tutorials will help you:
- Practice important data handling skills with textual data
- Learn about the ways text analysis can be applied
- Extract relevant insights from real-world data.
The tutorial is organised into four case studies, each with its own data set:
- Transcripts of TED talks
- A collection of comedies and tragedies by Shakespeare
- One month of newspaper headlines
- Song lyrics spanning five decades
Further support can be found in the tidy text mining book, which available online.
The LSE Library has secured a licence to use ProQuest TDM Studio. ProQuest TDM Studio is a platform for text and data mining across the Library's current ProQuest subscriptions. Features of the ProQuest TDM Studio platform include:
- Access data from the ProQuest library of resources, which includes videos, books, journal articles, and newspapers
- Use pre-made scripts to extract the data you want
- Either extract the data to use in a different platform, such as NVivo or QDA Miner, or do analysis within the TDM Studio environment using R and Python
- The workbench dashboard feature allows analysis to be done across the majority of the Library's ProQuest subscriptions using R and Python
- Visualisation dashboard has a graphical user interface with pre-built visualisations
ProQuest TDM Studio is available by request only. To request an account, contact the data library.
Quantitative Data
Analysis of quantitative data involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to describe, predict, or control variables of interest. The Digital Skills Lab is currently running workshops in SPSS and Stata. You can find the booking links along with other resources below.